Iso Audit Checklist For Training Department Organizational Chart
- Iso Audit Checklist For Training Department Organizational Chart Depicting The Design Schematic Of Him Staff
- Iso Audit Checklist For Training Department Organizational Chart Template
- Iso Audit Checklist For Training Department Organizational Chart Ppt
Related Articles
- 1 How Can a Matrix Organizational Structure Promote Project Excellence?
- 2 What Are the Standard Elements of a Quality Management Plan?
- 3 Organization Structure & New Product Strategy
- 4 How do I Write a Quality Control/Quality Assurance Plan?
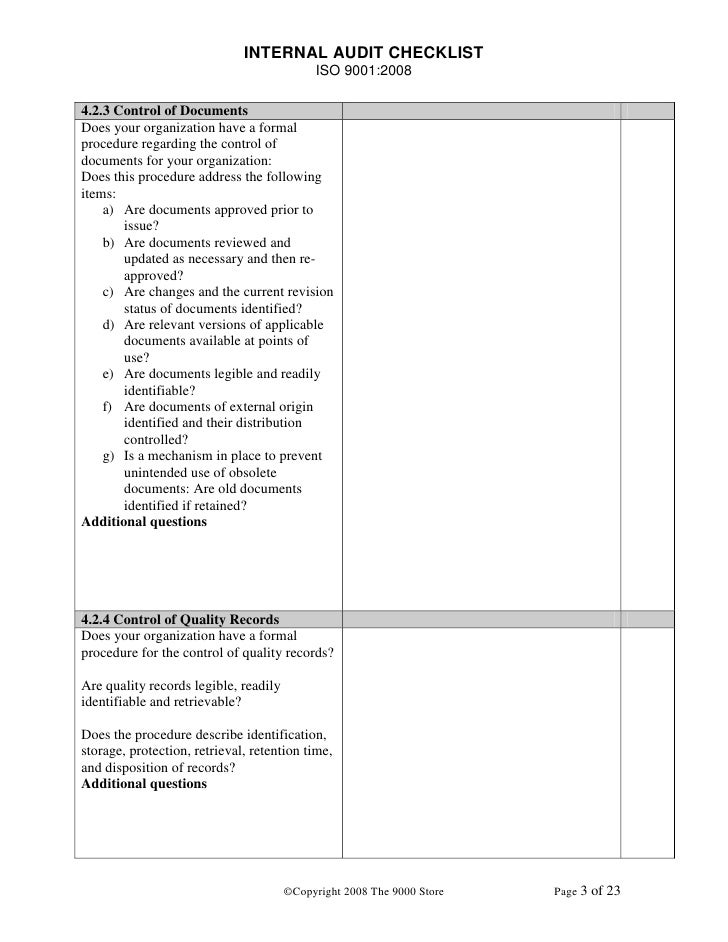
Internal Audit Checklist 4.2 Policy. Q Ensure that organizational chart is consistent with the. Their department and the benefits of following approved EMS. 7.1.4 Environment for the Operation of Processes No comments The environment for the operation of processes (in the ISO 9001:2008 Standard identified as work.
Quality assurance principles require an organizational structure that links responsibility for quality directly to the executive level of the company. Large organizations fulfill this requirement by appointing a quality assurance manager who reports to the CEO. The organizational structure also has to provide the QA manager with direct organizational paths into every department. Small businesses can meet these requirements by assigning the QA responsibilities to someone in management, giving him the authority to manage QA matters throughout the company and creating a QA reporting path to the executive level. Employees continue to report to their department manager for disciplinary and non-QA matters, but report to the person responsible for QA on quality questions.
Design
Quality assurance principles require the verification of all design work. In small businesses, designers can check their own work, but they have to do it as a separate process. On an organizational level, this means that the design department doesn't need a special quality function. All designers are responsible for the quality of their own work, under the supervision of the manager responsible for quality. They sign drawings and design documentation as designer and then check their work, initialing it when verified. They also keep track of revisions. The manager in charge of quality can use his organizational access to perform spot checks.
Sales and Marketing
Quality in sales and marketing means that sales and marketing material matches the documented characteristics of the company's products and services. Typically, sales personnel and marketing managers are responsible for the quality of the materials they create. The manager in charge of quality can use his organizational access to periodically review sales and marketing material. If he finds discrepancies, he may try to resolve them directly with the person responsible through his direct supervisory path in the organization. If he is not satisfied with the results, he can use his organizational access to the executive level to report the problem and suggest solutions.
Production
Production is a key company department for quality and normally requires its own quality function. Quality in a product means that the product corresponds with the needs and expectations of the customer. The two aspects of production quality are the specification of the product and its production according to the specification.

The responsibility for verifying that the specification matches customer needs and expectations usually rests with the manager responsible for quality. He makes sure production has the appropriate documentation. Within the production department's organization, responsibility for quality lies with testing. The production department assigns responsibility for quality to a member of the testing group who then reports to the manager in charge of quality on quality issues. The manager can use his organizational direct access to production to identify and solve problems or report them to the executive level of the company.
Human Resources

In human resources, quality means that job descriptions are clear, the required education and training is specified for each position and the personnel files include proof of the required education and training for each employee. The responsibility for quality lies with the department manager. The manager responsible for quality works with the department manager through the organizational link, giving him direct access to the department. Together, they verify that employee files satisfy quality requirements.
References (3)
About the Author
Bert Markgraf is a freelance writer with a strong science and engineering background. He started writing technical papers while working as an engineer in the 1980s. More recently, after starting his own business in IT, he helped organize an online community for which he wrote and edited articles as managing editor, business and economics. He holds a Bachelor of Science degree from McGill University.





